Research Areas
In each paradigm we focus on understanding the role of isolated 3'UTRs, 3'UTR sequences expressed in the absence of their cognate coding regions (3'UTR shown in red, CDS in green and protein in blue, in pictures below)
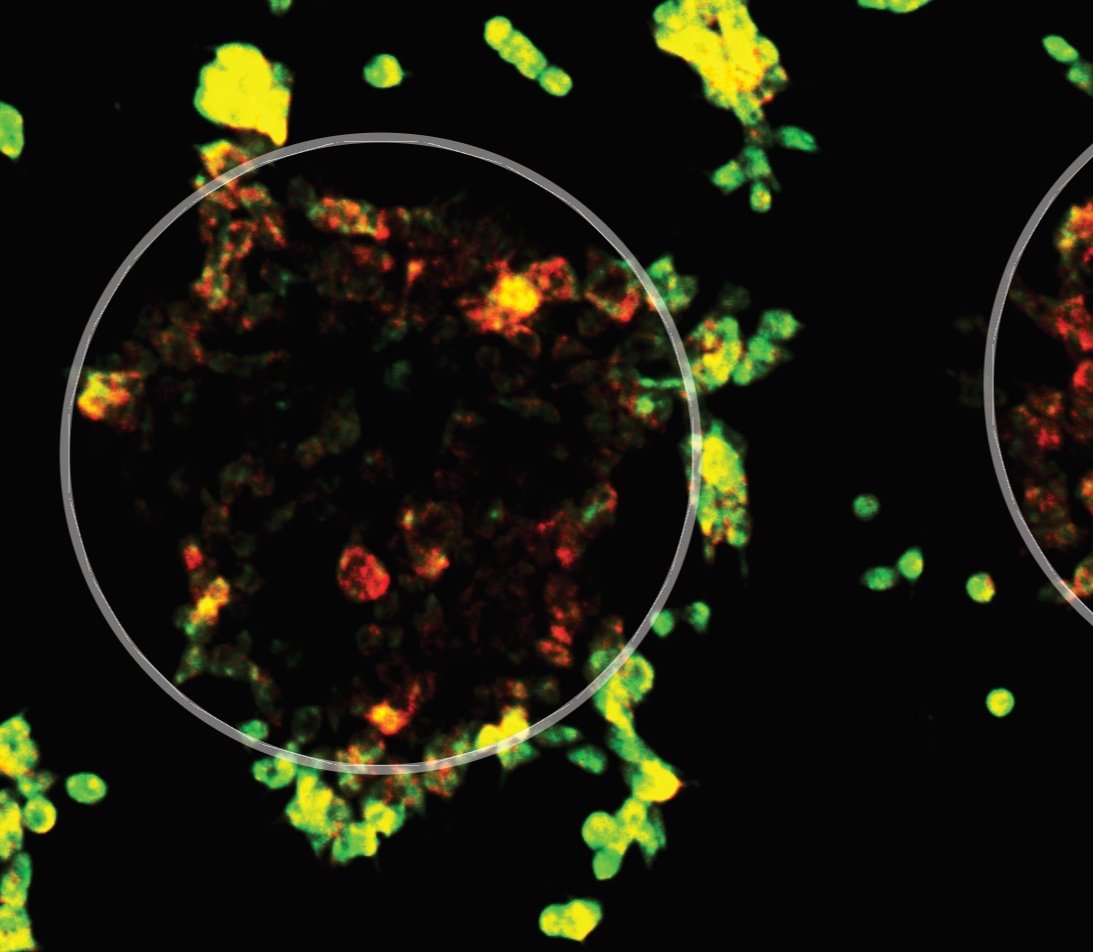
Pluripotent gene 3’UTR (red), cognate CDS (green), in human embryonic stem cell 2D organoid
Embryonic Stem cells
We are focused on the role of pluripotent gene i3’UTR and CDS in stem cell organization, proliferation and quiescence using bioinformatics, Crispr and other approaches.
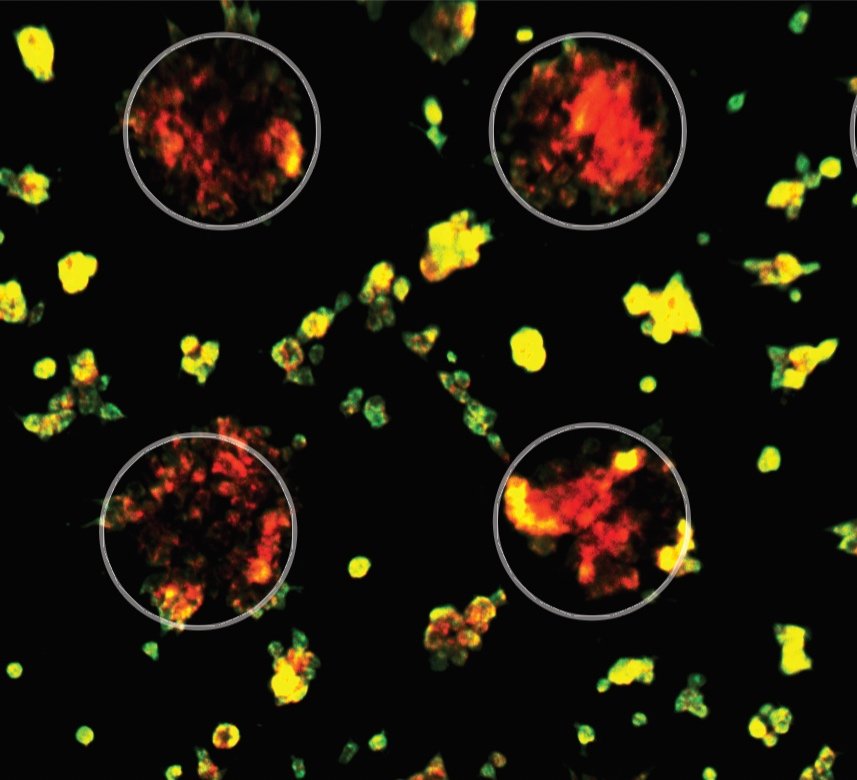
Cancer gene 3’UTR (red), cognate CDS (green), in human cancer cell line. Aggregated cells (in 2D organoid circles) express high 3’UTR, migrating cells switch to high CDS for the same gene.
Cancer
We are investigating the role of isolated 3’UTR expression in cancer progression, using bioinformatic and Crispr approaches in cancer cell lines, human cancer tissue and in vivo.
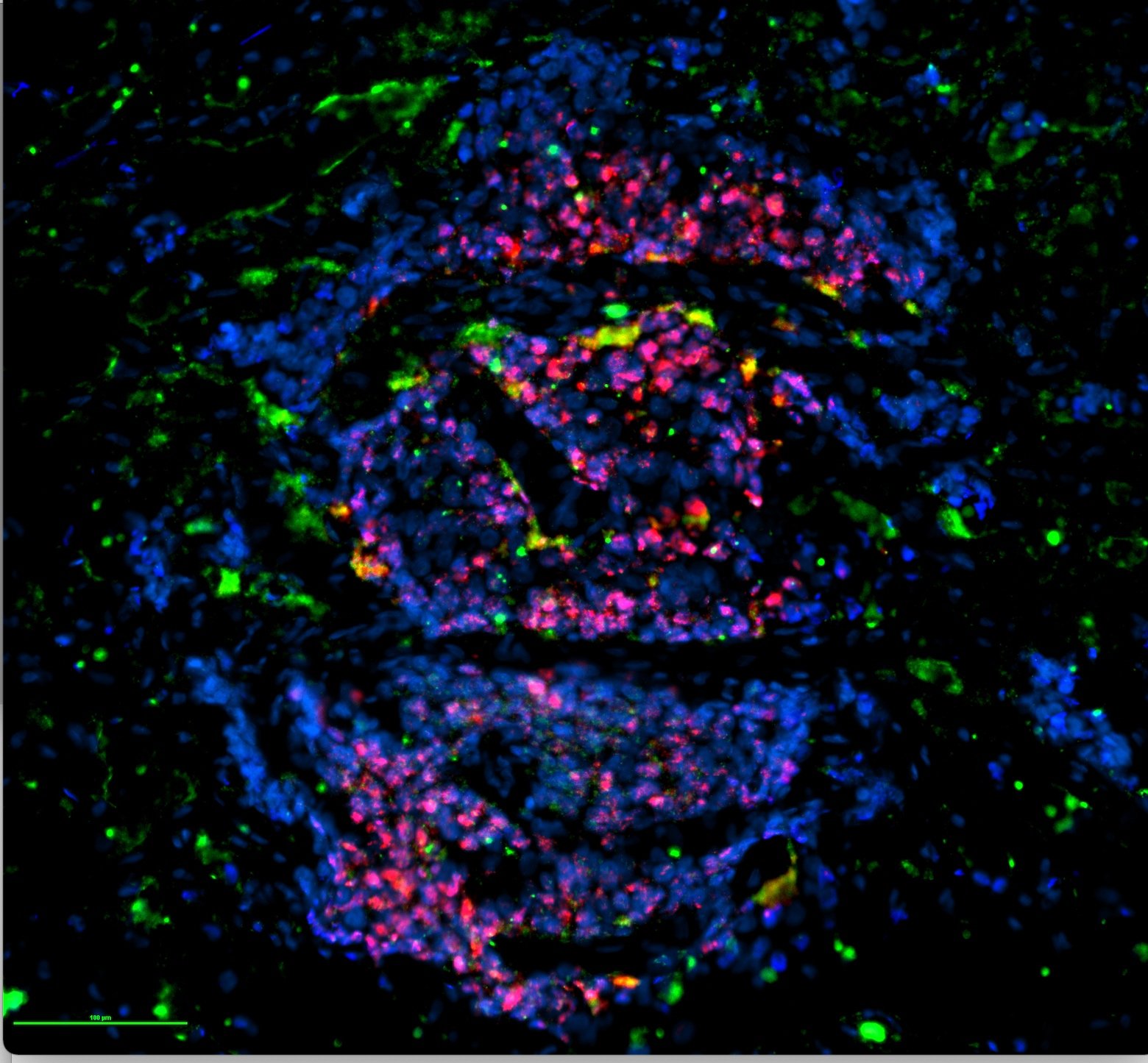
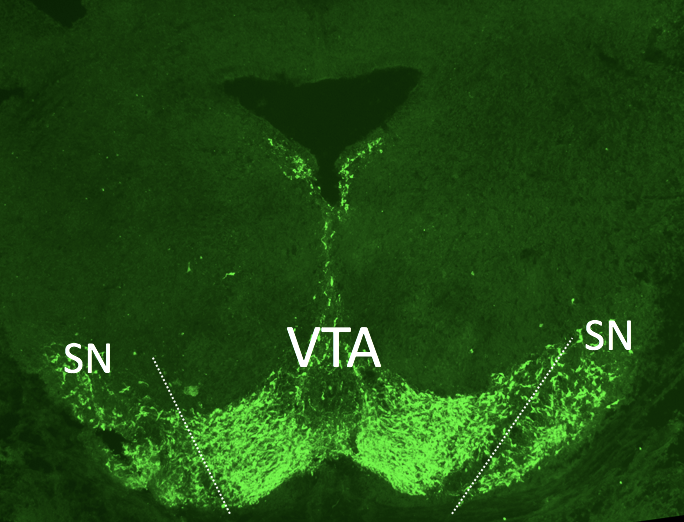
Developing mouse dopamine neurons (blue), transiently express the Nurr1 CDS (green), then switch back to Nurr1 3’UTR expression (red). Dorsal is up.
Neuronal development
Our lab has a long standing interest in developing dopaminergic neurons. Currently we are examining the role of i3'UTRs in the cell fate specification of developing dopamine neurons.